Apr. 09, 2024
Chemicals
DCS is a new type of computer control system compared to the centralized control system. It is developed and evolved on the basis of the centralized control system.
DCS is the English abbreviation of Distributed Control System, also known as distributed control system in the domestic automatic control industry.
DCS is a product that is highly integrated with computer technology, control technology and network technology. DCS usually uses several controllers (process stations) to control many control points in a production process. The controllers are connected through the network and can exchange data. The operation uses a computer operating station, which is connected to the controller through the network to collect production data and convey operating instructions. Therefore, the main characteristics of DCS can be summed up in one sentence: decentralized control and centralized management.
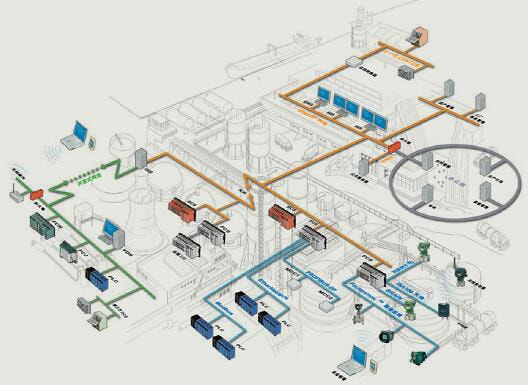
Structurally speaking, DCS includes process level, operation level and management level. The process level is mainly composed of process control stations, I/O units and field instruments, and is the main implementation part of the system control function. The operation level includes: operator station and engineer station, which complete the operation and configuration of the system. The management level mainly refers to the factory management information system (MIS system). As a higher-level application of DCS, there are currently few systems applied to this level in the domestic paper industry.
The control decision-making of DCS is completed by the process control station, so the control program is executed by the process control station.
The process control station of DCS is a complete computer system, mainly composed of power supply, CPU, network interface and I/O
The control system needs to establish signal input and output channels, which are I/O. The I/O in DCS is generally modular. An I/O module has one or more I/O channels used to connect sensors and actuators (regulating valves).
Usually, a process control station is composed of several racks, and each rack can place a certain number of modules. The rack where the CPU is located is called a CPU unit. There can only be one CPU unit in the same process station. The other racks used only to place I/O modules are I/O units.
The I/O unit and the CPU are connected via a fieldbus.
Fieldbus is a digital network used in process control sites. It not only includes the exchange of process control information, but also includes the exchange of equipment management information. Through fieldbus, various intelligent devices (smart transmitters, regulators, analyzers and distributed I/O units) can easily exchange data, and process control strategies can be completely implemented at the field device level. Currently, the most commonly used fieldbuses are FUNDATION fieldbus (FF bus) and Profibus fieldbus. The application of fieldbus technology can conveniently connect various related intelligent devices and I/O units distributed in the control site to form a control system. This structure has become the development trend of DCS.
Currently, the commonly used systems are mainly SIEMENS' S7 and ABB's Freelance2000, in which the fieldbus used is PROFIBUS.
Network transmission speed is generally expressed in units of baud rate (Bps), which means the number of binary digits transmitted per second. Different networks generally have different baud rates, and the same network can also achieve different baud rates by using different network cables. For example: PROFIBUS fieldbus has a communication speed of 1.5KBps when using twisted pair as the network cable, and 12MBps when using optical cable. The Ethernet transmission speed using ordinary twisted pair cable is 10MBps, and it can reach 100MBps when using optical cable. In addition, the length of the transmission distance will affect the transmission speed. Generally speaking, the longer the distance, the slower the speed.
The process of defining a system through specialized software is configuration. The process of defining the arrangement position and type of each module of the process station is called process station hardware configuration; the process of defining the control strategy and control program of the process station is called control strategy configuration; the process of defining the operator station monitoring program is called operator station configuration; The process of defining the system network connection method and the addresses of each station is called network configuration.
PLC is a programmable logic controller.
Early PLCs were only used to complete some electrical logic control and switching values. Today's PLCs have greatly improved in performance, especially in their ability to process analog signals, so PLCs can now be used for process control.
Analog quantity refers to a continuously changing signal (such as 4~20mA, 0~5v); digital quantity refers to a signal that only has a switching state.
Commonly used I/O signals are generally divided into: AI, AO, DI and DO. AI——Analog input signal. AO——Analog output signal. DI - digital input signal. DO——Digital output signal.
The openness of DCS refers to the ability of DCS to easily connect to third-party systems or devices through different interfaces and obtain their information. This connection is mainly realized through the network. The use of universal, open network protocols and standard software interfaces guarantees the openness of DCS. The DCS system currently adopted by our company has very good openness.
In some applications that require high system reliability, the DCS design needs to consider hot backup, which is system redundancy. This means that some key modules or networks in the system are designed to have one or more backups. When the current working When some problems occur, the system can automatically switch to backup through special software or hardware, thus ensuring uninterrupted operation of the system.
Commonly designed redundancy methods include: CPU redundancy, network redundancy, and power supply redundancy. In extreme cases, some systems consider full system redundancy, which also includes I/O redundancy.
Different from redundancy, I/O margin is just that the number of I/Os in the system is greater than the application requirements. This margin is only quantitative, and the main purpose is to make it possible for the system to continue to add control signals in the future.
If you are interested in sending in a Guest Blogger Submission,welcome to write for us!
All Comments ( 0 )